| Range trading | |
| a share or an index often trades within a certain price range. Range trading is about buying at the low end of the range (on the hopes of a price rise to the high end of the range). Conversely, traders will sell at the high end of the range (on the hopes of a price fall towards the low end the range). | |
| Rebound | |
| this occurs when the price of an instrument starts to recover. | |
| Real time | |
| a computer system which updates constantly and shows an up to date picture is said to be operating in real time. | |
| Recession | |
| defined as two consecutive quarters of negative economic growth as measured by a county's gross domestic product (GDP). | |
| Recovery Stocks | |
|
These are the shares of companies which have been going through a difficult path. They may be firms which have been successful in the past, but which have seen a drop in profits because the general market is poor, or they may be shares which have not met investor's expectations, or which are failing. If you bet on these shares when they have hit the bottom of the cycle, or at the end of the recession, you could bet on them making a large and unexpected gain when they start to move up again. |
|
| Redemption | |
| The date when the nominal value of a stock will be repaid to the holder. | |
| Redemption yield | |
|
The yearly return you get from a fixed interest stock which you hold until it is redeemed. It consists of two parts: the interest, often after tax, and the averaged out difference between what you paid and the value at redemption. |
|
| Red Herring | |
| A term used for preliminary prospect uses for a new issue used to measure market sentiment for the in the security. The key figures on such an announcement, such as the profit forecast, will always be deliberately left blank. | |
| Reduced spreads | |
| smaller differences between selling and buying prices. | |
| Refinancing | |
| Paying off an existing loan with another loan or equity issue.. | |
| Registered stock | |
| Stock in which the name of the holder is listed in the company's register and the stock is transferable only by his signature on a stock transfer form as opposed to bearer stock which is transferable by delivery. | |
| Regulation S | |
|
Regulation S was crafted as a safe harbor that allows US public companies to sell shares to non-U.S. citizens. In essence, while regulators wanted to assure that U.S. investors had adequate access to information about public companies, non-U.S. residents were not afforded the same protection. Those non-U.S. residents would be permitted to buy and sell shares, among themselves, even though the issuer had never registered those shares with the SEC. In other words, companies were given license to do abroad what they could not do at home - dump shares on the marketplace without registration or disclosure. To qualify for a Regulation S exemption, the shares must be sold offshore to a non-U.S. resident, and may not be sold back into the United States for one year. Those requirements are not as stringent as they may seem at first blush. The U.S. market is foreclosed to re-sales for one year, but that leaves the rest of the world - and the market for U.S. public companies is thriving around the globe. |
|
| Relative Strength | |
| Share performance compared with a specified index. | |
| Relative Strength Index (RSI) | |
| One of the most widely used indicators by short-term traders is the Relative Strength Index (RSI). The Relative Strength Index or RSI is a technical analysis indicator which measures the magnitude of recent gains of a stock or index over a given time period against the magnitude of losses over that period. The RSI ranges from 0 to 100 and is usually calcuated using over the last 14 periods. A measure of strength where you compare the performance of one thing against another. It's commonly used to measure the strength in price action of a stock against it's market index. As such RSI compares the number of days that an index finishes higher against the number that it ends lower. It ranges in value from 0 to 100 and is generally considered to be showing overbought conditions if it reaches 70 or more and oversold if it approaches 30, although some traders prefer to use 80 and 20 respectively. This is because technical analysts believe an RSI value of 30 or below indicates a market is oversold and a value of 70 or above indicates a market is overbought. It doesn't compare the relative strength of different securities as the name suggests, but it only shows the performance of just one security. | |
| Renunciation | |
| The giving up of the right to be registered as the holder of a new issue, enabling the issue to be transferred to another. | |
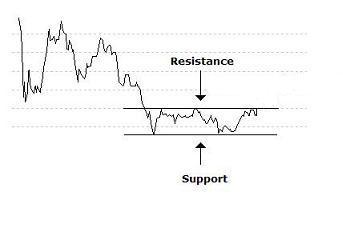
| Resistance | |
| A level or zone where sellers in a market keep the price from moving higher. When a company's share price fails to get above a certain price level this level is deemed to be resistance. Resistance occurs when there are lots of sellers at a particular price level, so each time the share price reaches this level the price typically falls back due to increased selling pressure. Technical analysts believe share prices can go much higher once they eventually clear an area of strong price resistance. The opposite of Resistance is Support. | |
 |
|
| Resistance level | |
| Resistance is a price level at which a security or index will tend not to rise above or struggles to break through, either for technical reasons regarding the price or psychological ones, for example gold rising above $2000 per ounce. A resistance level is a price. In other words, a price level identified by technical analysts at which persistent selling of a share or commodity takes place. For example, if the share price history of company X is plotted on a chart, and the chart shows that the share never seems able to rise above £4.20 or fall below £3.60, then the resistance level is £4.20 and the support level is £3.60. The significance of this is that if a share price does break through its resistance level, you could make a profit from the subsequent rise in price. | |
| Retained earnings | |
| Is the money left over after the company has paid dividends. These funds drive the company's growth. This why it's advisable to look for companies with dividend payout ratios of less than 70%.. | |
| Retail sales | |
| purchases of goods and services by consumers. | |
| Return on Capital | |
| Is a measure of the return the management has been able to achieve on the capital invested in the business. ROC = EBIT / Total Assets - Current Liabilities Note: Return on capital is also called 'Return on Invested Capital'. |
|
| Return on capital employed (ROCE) | |
| Stands for return on capital employed. Shows how well the directors are sweating the company's assets. In other words, a ratio that shows the efficiency and profitability of a company's capital investments. Calculated as earnings before interest and tax (EBIT): (Capital employed + Short term borrowings - Intangible assets). |
|
| Return on Assets | |
| Is a measure of the return a company's management has been able to achieve on the assets invested in the business. It's calculated by dividing net income by average total assets for the period. | |
| Return on Equity | |
| Return on Equity (ROE) is a measure of how well a company used reinvested earnings to generate additional earnings. ROE is as such a measure of the return the management have been able to achieve on shareholders funds. It is calculated by dividing net income by shareholder’s equity. Shareholder's equity is equal to total assets minus total liabilities. | |
| Return on Investment | |
| Return on Investment (ROI) is a measure of the profit from your investment divided by the investment itself (usually expressed as a percentage). | |
| Revenue | |
| Is the money coming into the business from normal business operations. The money might not actually have been received yet, but it is booked up. Note: Revenue is also called 'sales'. | |
| Reversal Day | |
| A term used to describe the day on which a security makes a significant change of direction in terms of its price. The term is not applied until the security has made a significant change in the opposite direction to the previous trend. | |
| Rights issue | |
| A means of raising more cash by issuing extra shares. Usually the new equity is offered at a discount to ensure investors subscribe. If a company needs to raise capital - to buy another company or develop a product - it may consider a rights issue. It invites its shareholders to buy additional shares, and the number you can buy will depend on how many you already own. Because this creates more shares in the company, their value will fall, so, to compensate, extra shares will be offered at a discount. | |
| Risk | |
| the possibility that the real return of an investment will be worse than expected. This could mean losing some, or all, of the original investment. | |
| Risk reward ratio | |
| how much you are willing to risk for the chance of a good profit. It may be worth risking 50 points to make 100 points, but it may not be worth risking 50 points to make 30 points. | |
| Rolling contract | |
| A spread bet with no fixed expiry date, or an expiry date years in the future. | |
| Rolling daily bet | |
| A spread bet contract that automatically closes and then re-opens at the same mid-price each business day until it is closed.. | |
| Roll over | |
| Rollover is the closing of an open bet and the opening of a new bet for the same amount at a point in time; typically incurs a charge for futures style bets. It allows you to transfer a trade that is near its expiry date to the next expiry date. On the contract expiry date you have the option of rolling over an open trade to the next contract expiry month. Typically this involves closing out your current position (at either a profit or loss based on the close-out price) and opening up a new position. Rolling over is a facility offered by a spreadbetting fir to those clients whose financial positions are due to expire within a short time and want to roll them into the next contract month. Normally clients can roll positions from the expiring contract to the next contract month for a reduced spread. | |
| RSI | |
| Relative strength indicator. A technical indicator based on the momentum of prices in a preceding 14-period block. A reading above 70 (out of 100) is classed as 'overbought'; a reading below 30 is deemed oversold. | |