
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a digital currency or so called “cryptocurrency” introduced as open source software in 2009 by a developer or group of developers under the name Satoshi Nakamoto. With no influence of big corporations or central banks it is purely controlled by a mathematical algorithm. For online retailers, Bitcoins are an interesting proposition since they don’t attract the large fees associated with credit cards.
It is widely believed that the first Bitcoin trade for goods or services took place on May 21, 2010 when Laszlo Hanyecz, a programmer living in Florida, sent 10,000 Bitcoins to a volunteer in England who ordered two pizzas for Hanyecz at a cost of US$25.
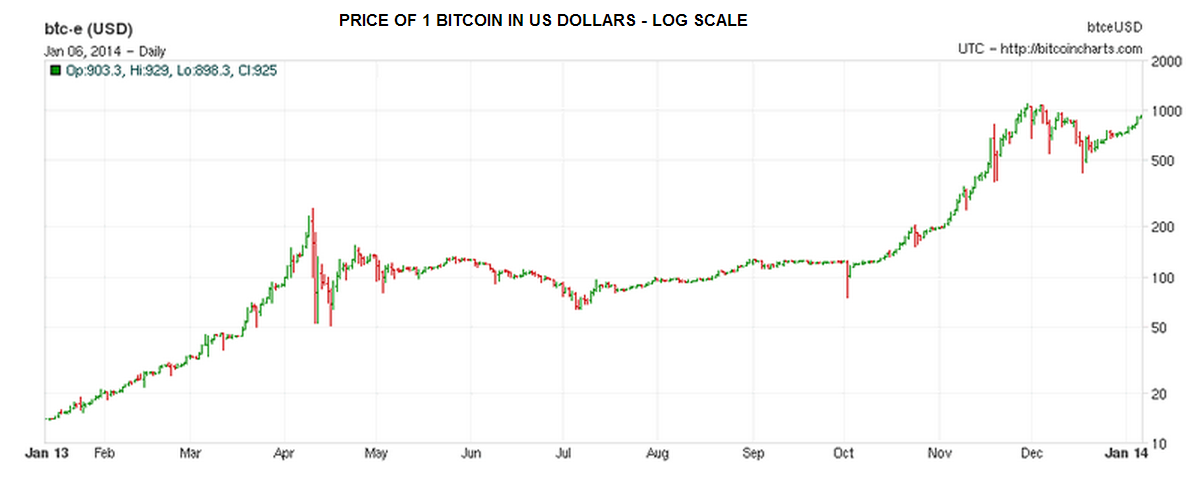
The total value of Bitcoin has risen from $150m to $10bn in the past year, though a significant rise, this is still tiny versus the $1.2 trillion circulating in U.S. dollars.
How does Bitcoin work?
The system uses cryptography to control the creation and transfer of Bitcoins. Buyers of the coins known as miners verify and timestamp transactions into a shared public database called the block chain and send payments by broadcasting digitally signed messages to the network. The first client software, the so called, Satoshi client, has been enhanced by developers due to open source coding and is known as Bitcoin-Qt. It is sometimes referred to as the reference client because it serves to define the Bitcoin protocol and acts as a standard.
The system is maintained by a decentralised peer-to-peer database recording every transaction in the history of the currency and it uses public-key cryptography, in which pairs of cryptographic keys, one public and one private, are generated. Transactions do not explicitly identify the payer and payee by name and a transaction transfers ownership from one Bitcoin address to another meaning the system is anonymous with its obvious appeal for those with criminal intentions.
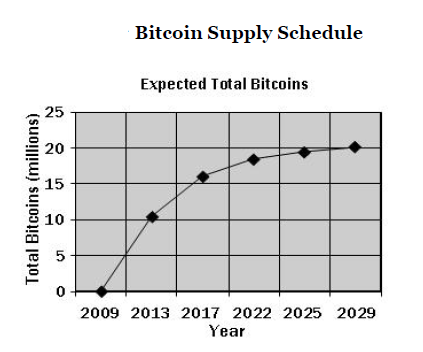
Bitcoin’s money supply is predefined by the Bitcoin protocol unlike normal currencies controlled by central banks such as the U.S. Federal Reserve which have the power to print money whenever they like. Currently there are over twelve million Bitcoins in circulation, with a creation rate of 25 bitcoins approximately every ten minutes. The total supply is capped by 21 million.
Users send and receive payments using client software and approximately every ten minutes, a block of transactions is confirmed to a shared public record called the block chain that prevents double spending and acts as a ledger of every Bitcoin transaction by Bitcoin address. This confirmation process, known as “mining”, carries a reward of 25 bitcoins per block for the providers of this service.
The block reward will be halved to 12.5 bitcoins in 2017 and again approximately every four years thereafter. By 2140 there will be approximately 21 million bitcoins in existence and transaction processing will be solely incentivised by transaction fees.
Bitcoins are bought and sold at a variable price against the value of other currencies through a system of exchanges, the most notorious of these by the now defunct Silk Road. The China-based Bitcoin exchange, Japan-based Mt.Gox and Europe-based Bitstamp are the largest.
By the end of November 2013 the total market capitalisation of all Bitcoins in existence exceeded US$10 billion for the first time.
The Drawbacks
When it was created the Bitcoin system promised to be a new type of money. Normally a form of currency is is a medium of exchange, obviating the need for barter; a store of purchasing power; and a stable unit of account that serves as a standard of cost.
Though designed as on online transaction vehicle, in respect of stability, Bitcoins have been a failure with volatility caused by huge speculation and an insufficient amount of the currency. Additional problems are significant and one of the key areas of worry for users is theft by hackers obtaining encryption passwords through 3rd parties or using Trojan horse malware. It has been found that automated programmes, co called bots, are engaging in covert mining of bitcoins
Bitcoin has also been used by crooks to launder money. In 2013 the FBI shut down the Silk Road online black market and seized 144,000 Bitcoins worth $28.5 million at the time as the currency was being used to buy illegal drugs and firearms.
The biggest drawback is that bitcoins lack intrinsic value because their value is not backed by hard assets or the full faith and credit of a sovereign government.
In March 2013 a technical glitch caused a fork in the block chain with one half of the network adding blocks to one version of the chain, and the other half adding to another other. For six hours there were effectively two Bitcoin networks operating at the same time, each with its own version of the transaction history. The core developers called for a temporary halt to transactions, sparking a sharp sell-off.
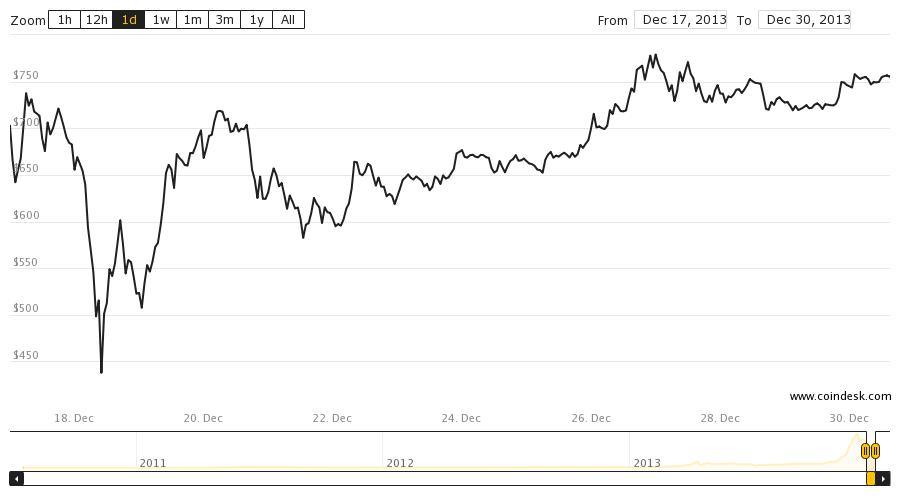
On 5 December 2013, the People’s Bank of China announced it was prohibiting Chinese financial institutions from using bitcoins, the price of bitcoins collapsed in December 2013 as a result on restrictions imposed in China. They traded as low as $422 around December 18th, when the large Chinese exchange BTC China acknowledged that it wasn’t accepting new deposits in the local currency until it could find a new payment processor that would do business with it.
Many governments are reviewing their tax status. Britain’s HM Revenue and Customs has advised traders that it is looking at alternatives to the current 20 per cent value added tax on purchases of the coin.
Bitcoin – the Future of Money?
Satoshi Nakamoto’s dream of an autonomous currency is an interesting one with Central Banks around the world clearly keeping a close eye on developments. Is this a return to a system similar to the Gold Standard? Maybe, but a system based on a physical asset that can be sold to realise value is very different to a digital algorithm with all the risks of hacking and fraud. It is hard to see how the U.S. dollar, Euro and Yen are going to be displaced any time soon.
At the moment relatively few companies are willing to accept Bitcoins as a transactional currency and this is not surprising given their extreme volatility. Stability is key and the Bitcoin system has a long way to go in that respect. Still at least you know how many Bitcoins are going to exist in the near future unlike the U.S. dollar!
Contrarian Investor UK
by contrarianuk
Is Bitcoin really the currency of the future?
Jan 21, 2014 at 2:22 pm in Market Commentary by contrarianuk
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a digital currency or so called “cryptocurrency” introduced as open source software in 2009 by a developer or group of developers under the name Satoshi Nakamoto. With no influence of big corporations or central banks it is purely controlled by a mathematical algorithm. For online retailers, Bitcoins are an interesting proposition since they don’t attract the large fees associated with credit cards.
It is widely believed that the first Bitcoin trade for goods or services took place on May 21, 2010 when Laszlo Hanyecz, a programmer living in Florida, sent 10,000 Bitcoins to a volunteer in England who ordered two pizzas for Hanyecz at a cost of US$25.
The total value of Bitcoin has risen from $150m to $10bn in the past year, though a significant rise, this is still tiny versus the $1.2 trillion circulating in U.S. dollars.
How does Bitcoin work?
The system uses cryptography to control the creation and transfer of Bitcoins. Buyers of the coins known as miners verify and timestamp transactions into a shared public database called the block chain and send payments by broadcasting digitally signed messages to the network. The first client software, the so called, Satoshi client, has been enhanced by developers due to open source coding and is known as Bitcoin-Qt. It is sometimes referred to as the reference client because it serves to define the Bitcoin protocol and acts as a standard.
The system is maintained by a decentralised peer-to-peer database recording every transaction in the history of the currency and it uses public-key cryptography, in which pairs of cryptographic keys, one public and one private, are generated. Transactions do not explicitly identify the payer and payee by name and a transaction transfers ownership from one Bitcoin address to another meaning the system is anonymous with its obvious appeal for those with criminal intentions.
Bitcoin’s money supply is predefined by the Bitcoin protocol unlike normal currencies controlled by central banks such as the U.S. Federal Reserve which have the power to print money whenever they like. Currently there are over twelve million Bitcoins in circulation, with a creation rate of 25 bitcoins approximately every ten minutes. The total supply is capped by 21 million.
Users send and receive payments using client software and approximately every ten minutes, a block of transactions is confirmed to a shared public record called the block chain that prevents double spending and acts as a ledger of every Bitcoin transaction by Bitcoin address. This confirmation process, known as “mining”, carries a reward of 25 bitcoins per block for the providers of this service.
The block reward will be halved to 12.5 bitcoins in 2017 and again approximately every four years thereafter. By 2140 there will be approximately 21 million bitcoins in existence and transaction processing will be solely incentivised by transaction fees.
Bitcoins are bought and sold at a variable price against the value of other currencies through a system of exchanges, the most notorious of these by the now defunct Silk Road. The China-based Bitcoin exchange, Japan-based Mt.Gox and Europe-based Bitstamp are the largest.
By the end of November 2013 the total market capitalisation of all Bitcoins in existence exceeded US$10 billion for the first time.
The Drawbacks
When it was created the Bitcoin system promised to be a new type of money. Normally a form of currency is is a medium of exchange, obviating the need for barter; a store of purchasing power; and a stable unit of account that serves as a standard of cost.
Though designed as on online transaction vehicle, in respect of stability, Bitcoins have been a failure with volatility caused by huge speculation and an insufficient amount of the currency. Additional problems are significant and one of the key areas of worry for users is theft by hackers obtaining encryption passwords through 3rd parties or using Trojan horse malware. It has been found that automated programmes, co called bots, are engaging in covert mining of bitcoins
Bitcoin has also been used by crooks to launder money. In 2013 the FBI shut down the Silk Road online black market and seized 144,000 Bitcoins worth $28.5 million at the time as the currency was being used to buy illegal drugs and firearms.
The biggest drawback is that bitcoins lack intrinsic value because their value is not backed by hard assets or the full faith and credit of a sovereign government.
In March 2013 a technical glitch caused a fork in the block chain with one half of the network adding blocks to one version of the chain, and the other half adding to another other. For six hours there were effectively two Bitcoin networks operating at the same time, each with its own version of the transaction history. The core developers called for a temporary halt to transactions, sparking a sharp sell-off.
On 5 December 2013, the People’s Bank of China announced it was prohibiting Chinese financial institutions from using bitcoins, the price of bitcoins collapsed in December 2013 as a result on restrictions imposed in China. They traded as low as $422 around December 18th, when the large Chinese exchange BTC China acknowledged that it wasn’t accepting new deposits in the local currency until it could find a new payment processor that would do business with it.
Many governments are reviewing their tax status. Britain’s HM Revenue and Customs has advised traders that it is looking at alternatives to the current 20 per cent value added tax on purchases of the coin.
Bitcoin – the Future of Money?
Satoshi Nakamoto’s dream of an autonomous currency is an interesting one with Central Banks around the world clearly keeping a close eye on developments. Is this a return to a system similar to the Gold Standard? Maybe, but a system based on a physical asset that can be sold to realise value is very different to a digital algorithm with all the risks of hacking and fraud. It is hard to see how the U.S. dollar, Euro and Yen are going to be displaced any time soon.
At the moment relatively few companies are willing to accept Bitcoins as a transactional currency and this is not surprising given their extreme volatility. Stability is key and the Bitcoin system has a long way to go in that respect. Still at least you know how many Bitcoins are going to exist in the near future unlike the U.S. dollar!
Contrarian Investor UK